Introduction to Virtual Reality Experiences
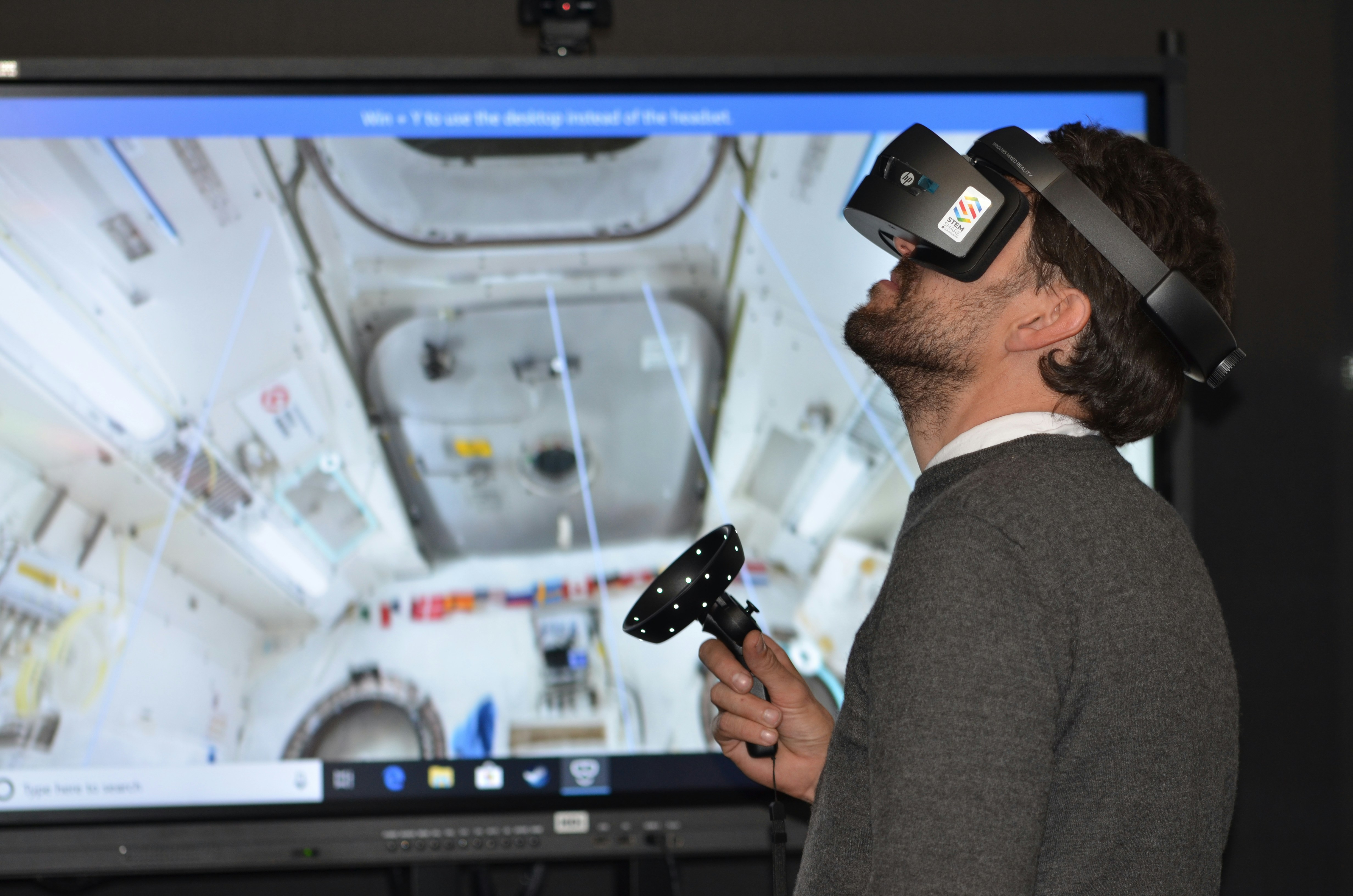
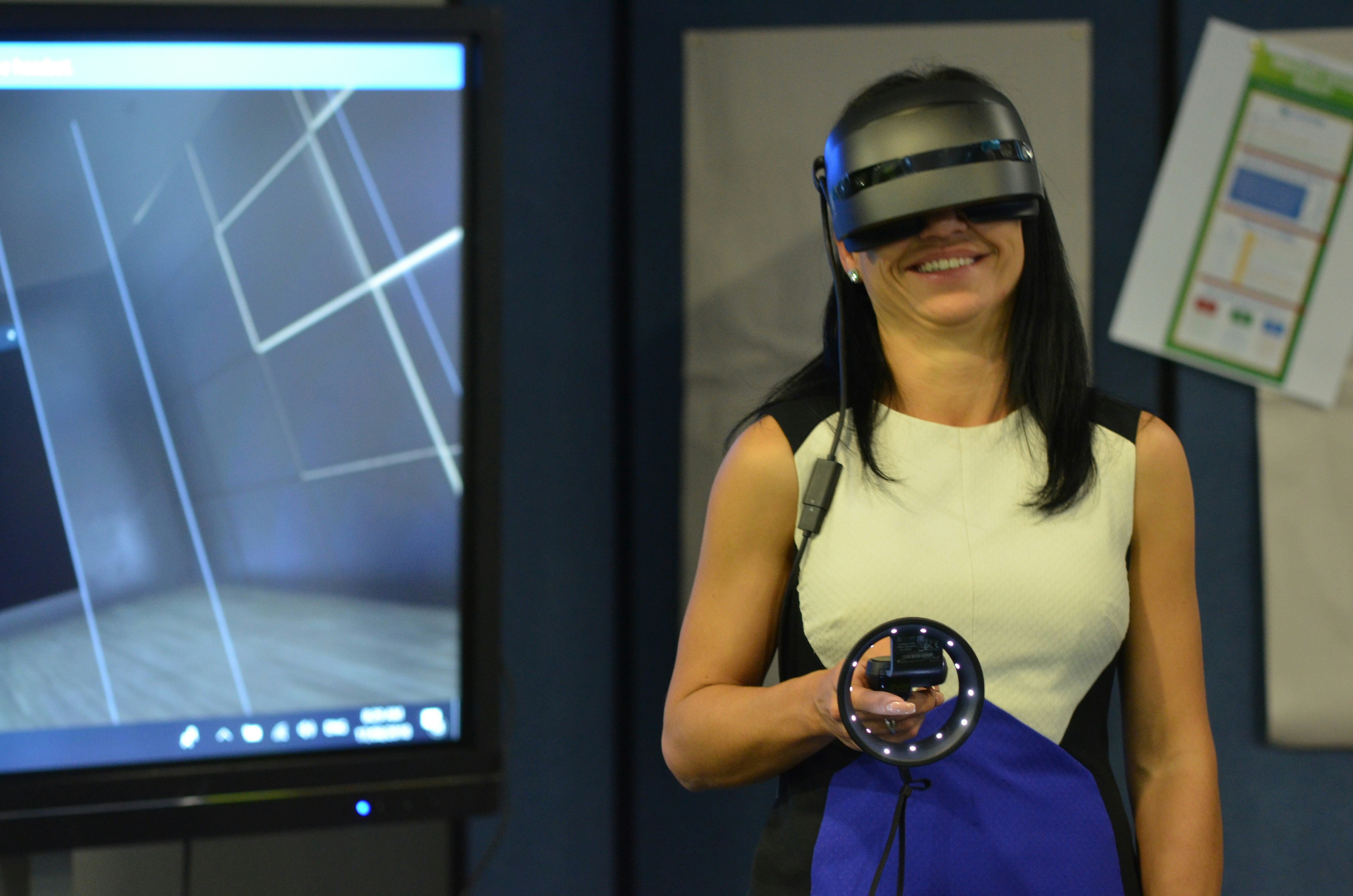
Virtual reality (VR) represents a transformative approach to how individuals interact with both digital and physical environments. By utilizing advanced technology, VR immerses users in a simulated reality that can replicate real-world experiences or create entirely new realms. This immersive experience is primarily achieved through VR headsets, which employ screens and optics to deliver vivid imagery designed to engage the user’s senses. The design of these devices focuses on providing users with a 360-degree view, allowing them to turn and explore their surroundings, thereby enhancing the sense of presence within the virtual world.
The significance of user experiences in VR cannot be overstated. Engaging multifaceted environments that allow users to interact with the world around them contribute to a more profound and memorable experience. A vital aspect of VR technology is its ability to blend elements from the physical realm with digital content, which creates a unique experience that can be customized to suit various applications, from gaming to training simulations, and even education.
With the rapid advancements in technology, the future of virtual reality is promising. Developers are continually finding innovative ways to improve the user interface and incorporate social, physical, and emotional factors into VR experiences. This evolution will not only enhance the quality of the immersive experience but also broaden the scope of applications for VR in various fields, such as healthcare and remote collaboration. As the line between digital and physical continues to blur, understanding the foundations of virtual reality experiences is essential for recognizing its potential and relevance in our increasingly interconnected world.
The Aesthetics of a Vibrant Virtual World
In the realm of blended virtual worlds, aesthetics play a pivotal role in shaping user experiences. The visual landscape is characterized by colorful environments that evoke creativity and curiosity. Lush digital forests with vibrant flora, expansive cities that glimmer with neon lights, and serene oceans with undulating waves all come together to create an immersive atmosphere. Throughout this virtual experience, users are met with a tapestry of colors and textures that stimulate the senses and foster engagement.
Dynamic environments amplify this aesthetic appeal. The virtual landscape is not static but constantly evolves, responding to user interactions. Imagine entering a gallery where the walls shift and change hue based on the artwork being viewed or walking through a city where the architecture morphs with the time of day. Such fluidity ensures that users are not merely spectators; they are active participants in an ever-changing world. This adaptability enhances the immersion, paving the way for deeper emotional connections to the digital space.
An intriguing aspect of this vibrant visual experience is the integration of floating data and holographic charts. These elements are seamlessly woven into the fabric of the environment, transforming essential information into artistic manifestations. For example, graphs can hover above a stunning landscape, displaying real-time statistics while maintaining an aesthetically pleasing design. The artistic direction behind these components is crucial, as it elevates data from mere numbers to forms of artistry that contribute to the overall visual appeal.
The design choices made in crafting these vibrant worlds influence users’ engagement dramatically. Color palettes, movement dynamics, and visual hierarchies are carefully curated to enhance usability while ensuring that the aesthetics remain engaging. Such thoughtful integration of visual elements creates a rich tapestry that not only delights the eye but also enriches the user experience in profound ways.
Interactivity: Engaging with the Environment
Interactivity in blended virtual environments plays a pivotal role in enhancing user experience and engagement. Through advanced technologies, users can manipulate data and interact with holographic displays, allowing for a more dynamic and immersive experience. This capability not only enriches the entertainment aspect of virtual reality (VR) but also serves practical applications in education and skill development. Users can explore various environments, conducting experiments, solving problems, and simulating real-world scenarios, all of which actively promote learning through experience.
The concept of user agency is central to interactivity in virtual worlds. When users can make choices and see the consequences of those choices in real time, their investment in the experience increases. This active participation contrasts sharply with passive forms of media consumption, such as watching television or reading a book. The ability to reshape the environment according to one’s decisions fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, further enhancing the immersive qualities of the VR experience.
Moreover, the design of interactive elements within virtual environments facilitates collaborative learning. Users can connect and work together, leveraging their individual strengths to achieve common goals, whether in a classroom setting or a corporate training program. Such collaboration not only builds essential social skills but also cultivates teamwork, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. As users engage in collective exploration, they can share insights and techniques, making the learning process richer and more effective.
In essence, the interactive capabilities of the blended virtual world redefine how users engage with information and their surroundings. By allowing manipulation of data and interaction with vivid holographic interfaces, these platforms encourage deeper connections between users and the virtual environment. As interactivity continues to evolve, it holds tremendous potential for education, making learning more effective, enjoyable, and accessible.
The Future of VR and Blended Environments
As we look toward the future of virtual reality (VR) and blended environments, it is essential to note the myriad technological advancements that are poised to reshape our interactions with digital spaces. Innovations in hardware, such as lighter headsets with improved resolution and haptic feedback systems, are aimed at creating more immersive experiences. These enhancements are likely to expand the applications of VR beyond gaming into critical sectors like education, healthcare, and remote work.
Within the educational domain, VR is anticipated to transform traditional learning methodologies. By immersing students in realistic simulations, educators can provide interactive lessons that promote engagement and retention of knowledge. From virtual field trips to complex scientific experiments, these experiences will make learning not just informative but also experiential. In the realm of remote work, blended environments will facilitate more meaningful social interactions and collaborative efforts, bridging the gap between physical and digital workspaces. Tools such as virtual offices may emerge, where employees can interact in real-time, enhancing team dynamics and productivity.
No discussion of the future of VR can overlook the potential for social interaction it offers. As virtual environments become increasingly sophisticated, users will find themselves engaging at a more personal level than ever before. The ability to create and customize avatars allows individuals to express themselves in ways that traditional social media cannot. These personalized experiences can foster stronger connections, alter perceptions of reality, and facilitate a richer form of digital engagement.
In conclusion, the trajectory of virtual reality and blended environments suggests an exciting future filled with possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, the applications of VR will undoubtedly expand, creating profound impacts across multiple sectors and enhancing user experiences. The journey into this blended virtual world is set to redefine how we learn, work, and connect in a digital age.