Understanding Virtual Reality
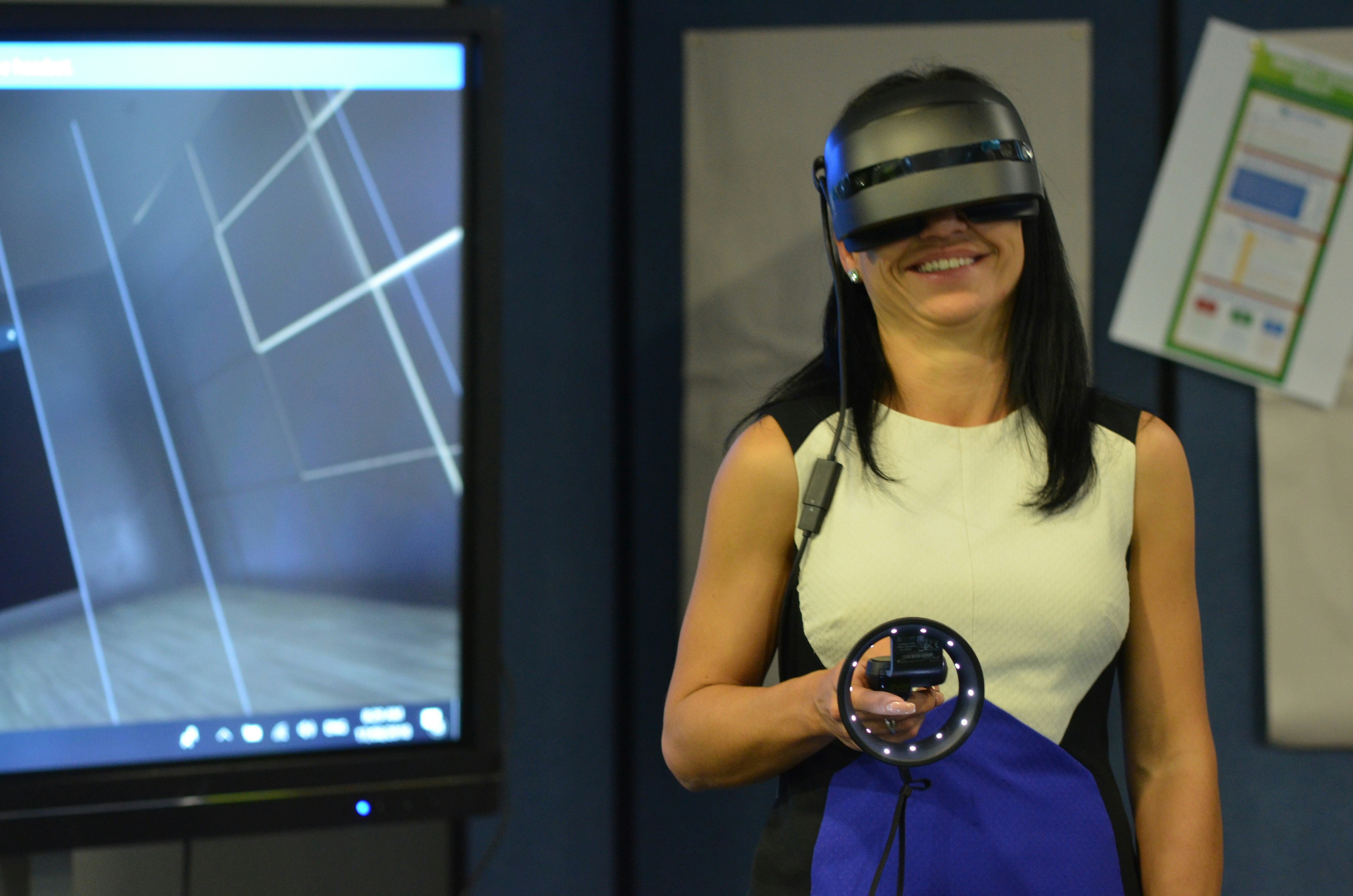
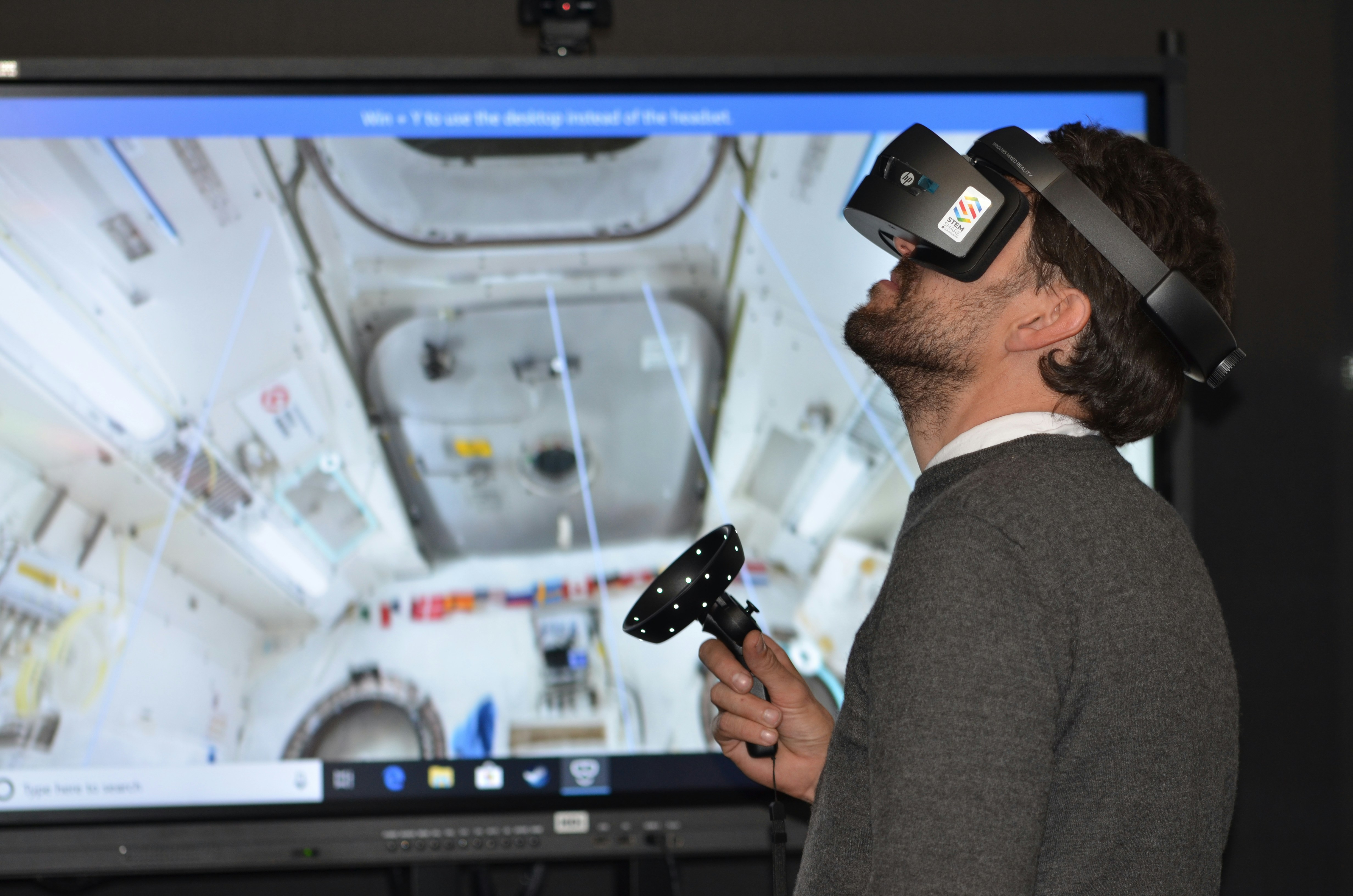
Virtual reality (VR) is an immersive technology that transports users into a fully digital environment, effectively isolating them from the real world. This digital immersion is achieved through the use of specialized hardware, including VR headsets that cover the eyes and often include headphones for auditory immersion. The primary goal of VR is to create an experience that feels as real as possible, allowing users to interact with a three-dimensional space through their movements and decisions.
At the heart of virtual reality technology is motion tracking, which captures the user’s physical movements and translates them into the digital world. This interaction is facilitated through controllers or gloves equipped with sensors, enabling users to manipulate objects, navigate through the environment, and even communicate with other participants in a multiplayer setting. Such innovative features create a sense of presence and agency, making the VR experience more engaging and dynamic.
Virtual reality has found applications across a variety of industries. In gaming, it offers players an opportunity to step into their favorite digital worlds and engage with them in a more visceral manner. Educational institutions leverage VR to simulate complex environments, allowing students to conduct virtual experiments or explore historical sites. Furthermore, training simulations utilizing VR technology can provide realistic scenarios for fields such as medicine, aviation, and military, where hands-on experience is crucial yet can be challenging to replicate in real life.
The sensations experienced within a virtual space can be profound. Users may feel weight, resistance, and even emotional responses due to meticulously designed environments. This level of engagement not only enhances entertainment but also enriches learning and training experiences, thereby expanding the potential of virtual reality in various professional domains.
Exploring Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) represents a transformative technology that overlays digital content onto the physical world, creating an interactive experience that blends both realms. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which transports users into a completely immersive digital environment, AR enhances real-world surroundings, allowing users to engage with both digital and physical elements simultaneously. This technology operates through various devices, most commonly smartphones and AR glasses, that use cameras, sensors, and advanced software to project digital images and information onto the user’s view of the real world.
One significant feature of augmented reality is its ability to recognize and respond to physical objects and environments. For instance, in retail, AR applications allow customers to visualize how clothing might look when worn or how home decor items fit within their living space. Such functionality not only enhances customer engagement but also enables consumers to make informed purchase decisions, thereby improving the overall shopping experience.
Healthcare is another sector where augmented reality has made substantial strides. Surgeons can utilize AR tools to overlay critical information onto their field of vision during complex procedures, improving precision and outcomes. Additionally, medical training programs leverage AR to simulate realistic surgical environments, allowing trainees to practice without endangering real patients. This innovative application underscores AR’s potential in enhancing professional education and operational efficiency.
The entertainment industry has embraced augmented reality as well, providing interactive gaming experiences that merge the digital and physical worlds. Popular mobile games, such as Pokémon GO, have successfully engaged millions by encouraging players to explore their surroundings while capturing virtual creatures layered over real environments. This level of interaction captivates users and emphasizes the potential of AR in delivering memorable and enriching experiences in leisure and recreation.
In conclusion, augmented reality offers a multifaceted approach to enhancing real-world experiences across various industries, fostering engagement and interaction while seamlessly merging digital content with our physical surroundings.
Key Differences Between VR and AR
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are two innovative technologies that, while often mentioned together, serve distinct purposes and offer different user experiences. One of the primary differences lies in user immersion. VR creates an entirely simulated environment that immerses users in a computer-generated world, typically experienced through a headset. This level of sensory immersion enables users to engage fully with the virtual space, indulging in experiences that range from gaming to virtual travel. On the other hand, AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital information onto physical surroundings, often through smartphones or AR glasses. This means users remain aware of and engaged with their actual environment while interacting with digital elements.
Technological requirements also differentiate VR from AR significantly. VR systems need robust hardware, including high-performance computers or specialized consoles, along with motion sensors and controllers for navigation. This complexity can involve higher costs. Conversely, AR can function on devices such as smartphones and tablets, which are more accessible and ubiquitous. While both technologies utilize advanced software and graphics capabilities, the hardware demands for AR are generally less intensive, making it easier to adopt in various settings.
Moreover, the applications of VR and AR differ. VR is often employed in sectors like gaming, training simulations, and immersive experiences, where complete immersion is paramount. Conversely, AR finds its uses across diverse fields, including education, healthcare, and navigation, allowing for enhanced information delivery within real-world contexts. Importantly, a notable trend is the potential integration of AR and VR, leading to mixed realities that could potentially offer users unique experiences by combining both immersive and interactive elements. Thus, understanding these key differences is essential for stakeholders across various industries looking to leverage either technology effectively.
Future Trends and Developments
As we glance toward the horizon, the realms of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) promise an array of transformative advancements. Both technologies are on the verge of significant growth, influencing various sectors such as entertainment, education, and professional environments. The evolution of VR and AR is not only characterized by technical improvements but also by their increasingly immersive experiences and interactive capabilities. With the rapid enhancement of hardware, including lighter headsets and more responsive tracking systems, the user experience is anticipated to become seamlessly integrated into everyday activities.
In the field of entertainment, VR offers increasingly sophisticated gaming experiences, while AR brings interactive elements to traditional media. The blend of real and virtual worlds can create dynamic storytelling, inviting audiences to engage with the content actively. In education, both technologies provide immersive learning environments, allowing students to explore complex subjects in engaging ways. Virtual simulations enable learners to practice real-world scenarios safely, while augmented reality can overlay educational content onto physical objects, enriching the learning process.
However, these evolving technologies also present potential challenges. Issues related to data privacy, mental health implications from excessive engagement, and ensuring equitable access are worth consideration. Moreover, as VR and AR become more integrated into society, there is a pressing need to address the societal implications of their use, particularly concerning user addiction and the digital divide that may exclude certain demographic groups from these advancements. Balancing innovation with ethical considerations will be crucial as the landscape of virtual and augmented reality continues to develop.
In conclusion, both virtual and augmented reality are set to redefine our interaction with the world. As these technologies advance, ongoing innovation will shape their applications, potentially revolutionizing sectors while necessitating a careful evaluation of the implications for users and communities alike.